Security and Trust¶
Overview¶
The business objects for Security and Trust capture the information needed to for each organisation to be able to enforce their own human resources and security policies. Because these policies are not common across the organisations, what is recorded is the information about security and trust. BDA platforms then use the security and trust information to enforce the local policies. For example, one company may require a senior manager to approve the release of a “confidential” model and only to organisations in the EU. Another organisation may require two senior managers to approve the release and only to organisations that have signed a “risk sharing partnership” agreement.
The Security and Trust objects are:
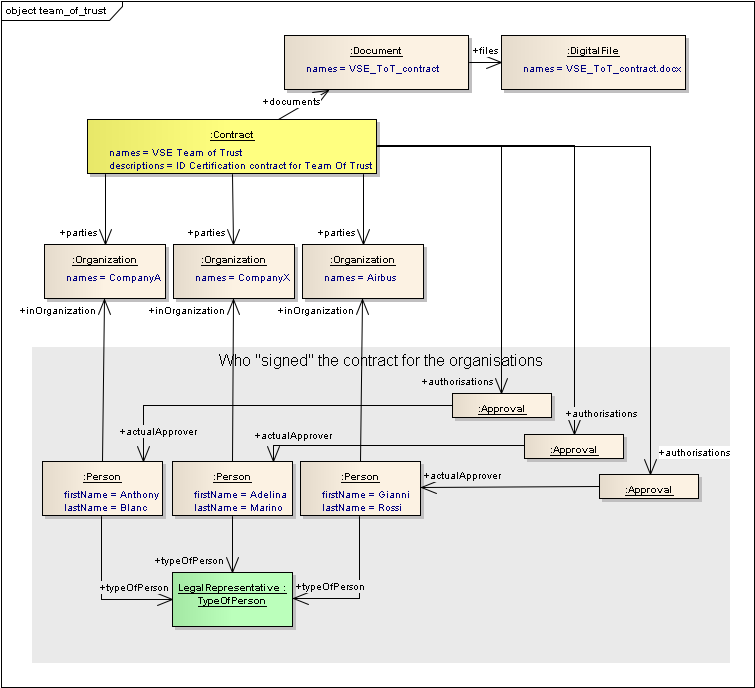
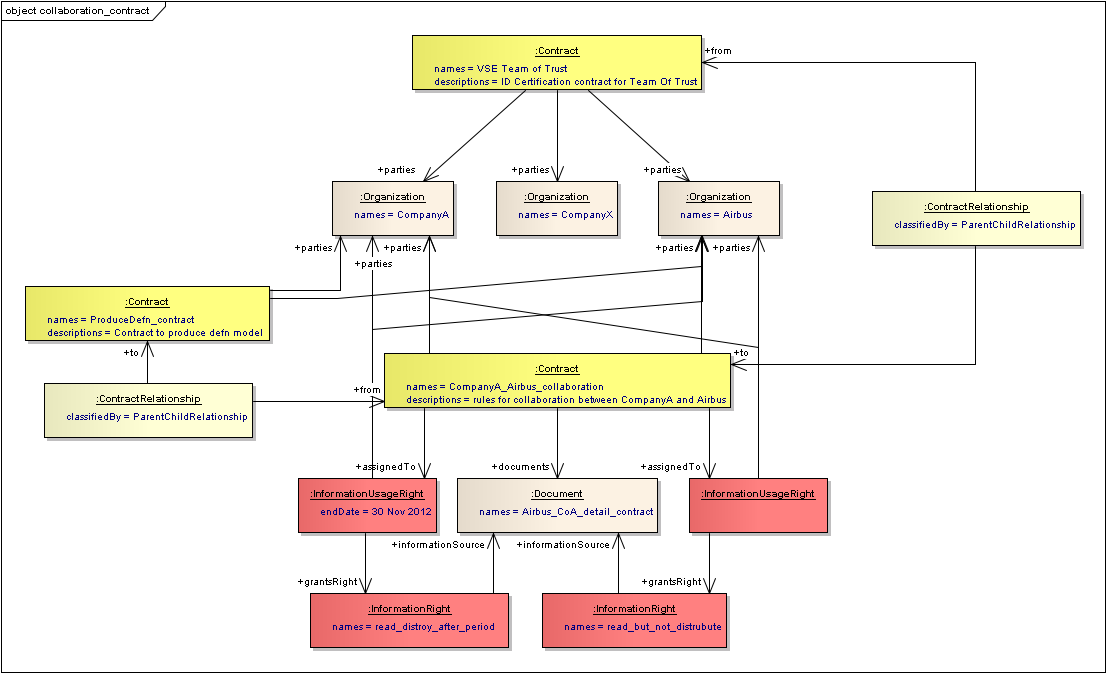
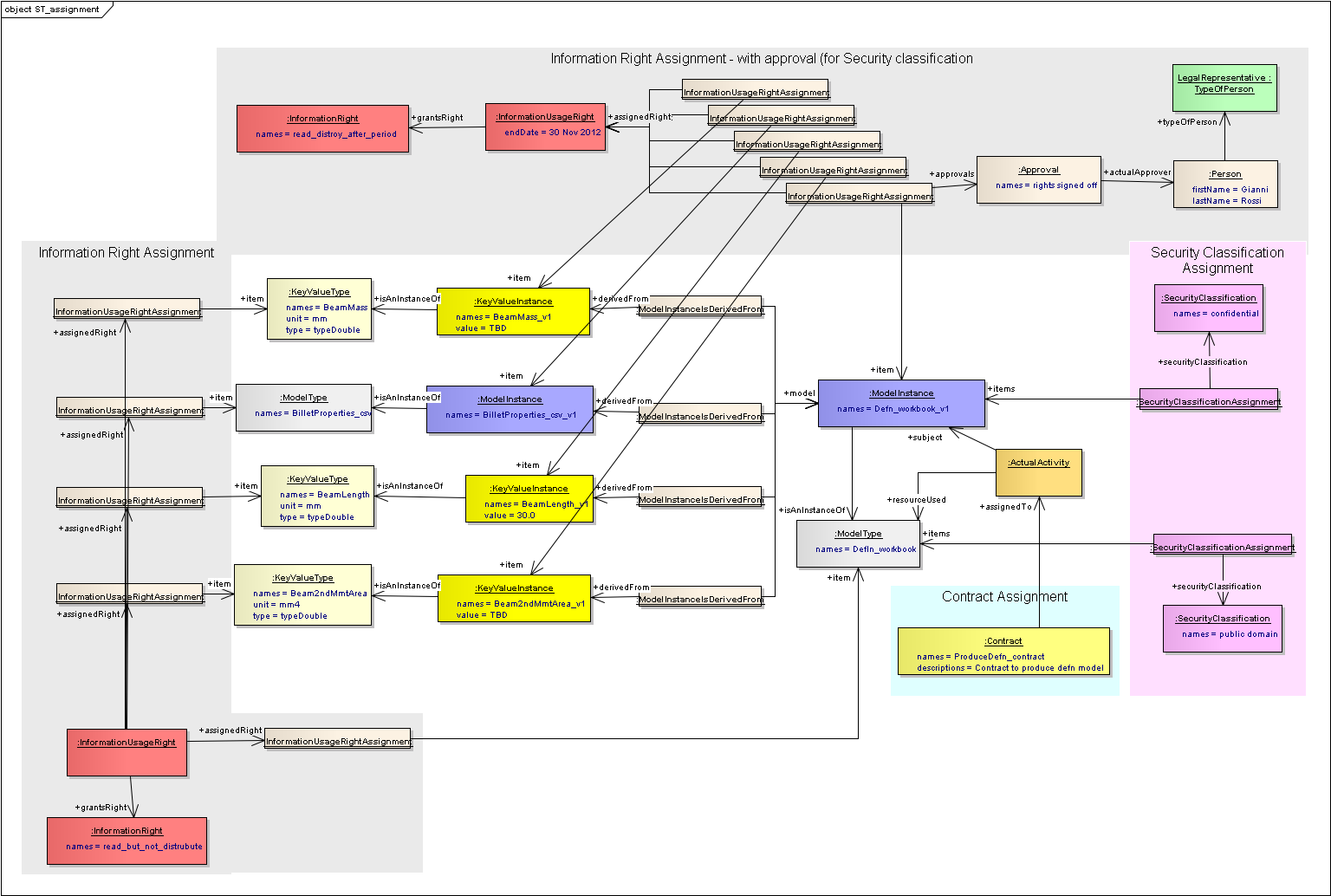
- Contract:
- A contract is an identifiable object that represents a binding agreement.
- It can have relationships to the organisation of people who are bound by the contract, and can also have approvals to show who “signed” the contract.
- It can point to documents(s) which is the actual contract (e.g. in a document management system)
- One contract can relate to other contracts, e.g. there could be a major partnership contract, and then many related contracts for the individual pieces of work
- A contract can point to the object(s) about which it is the agreement.
- For more information see: SysML - Contracts Diagram.
- Security Classification:
- Security classifications are ways to specify the level of security that is applied to something.
- It can have documents to describe the classification
- It can point to the object(s) to which it applies, and that assignment can have approvals e.g. there could be a business rule to say that all assignments of “Public Domain” classification must be signed by a manager.
- For more information see: SysML - Security Classifications Diagram.
- Information Right:
- This is to identify what may or may not be allowed for the information in the sense of legal rights or obligations. For example, it could be a standard clause in a contract, or the right to allow copies to be made only by Persons who are in a particular organisation but with the restriction that those copies must be destroyed at the end of the specified period.
- They have a source for the information right. This is a document, and will usually be a document that is also assigned to a contract.
- They can be assigned to objects(s) to grant the rights, in the context of a particular contract
- For more information see: SysML - Information Rights Diagram.
An illustrative example¶
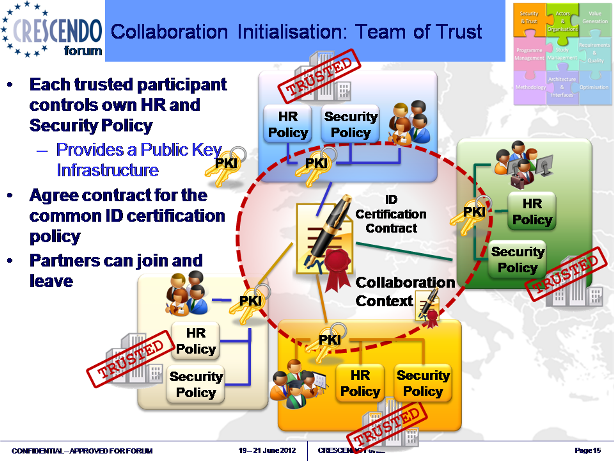
The Security and Trust objects can be associated with most of the business objects. The choice depends on the business rules and the scenario. In the example below there are two contracts for setting up the team of trust. The first is the “Collaboration context” contract which is associated to a contract to agree “ID certification”, i.e. so the partners in the team know you are who you say you are.
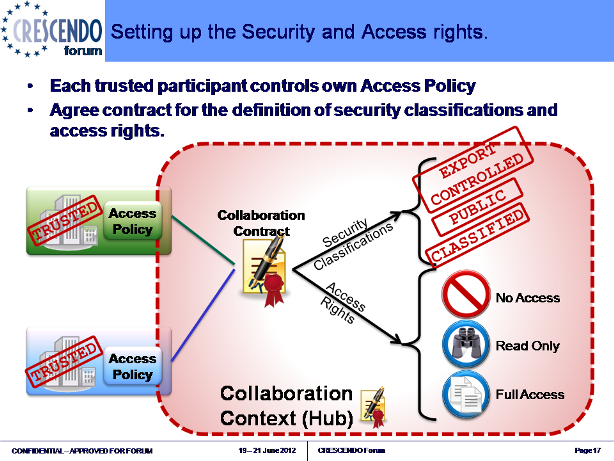
Associated to a Team of trust “Collaboration context” contract, can be a contract to agree the definition of the security classification and access rights that can be applied to objects that will be used for collaboration.
For more information see eLearn: Enterprise Collaboration > Module 3 > Highlight 6: Managing Intellectual Property in Collaboration